Protecting water quality with planting zones
The area where streams meet land is important for maintaining water quality. The September 7th Sustainable, Secure Food blog explains how use of buffer strips can protect water quality and ecosystems.
“The word ‘riparian’ refers to the place where streams meet land,” writes Amanda Ramcharan, Pennsylvania State University. ”This important intersection controls a lot of processes–especially with regard to water quality.”
Credit: ASA/CSSA/SSSA staff
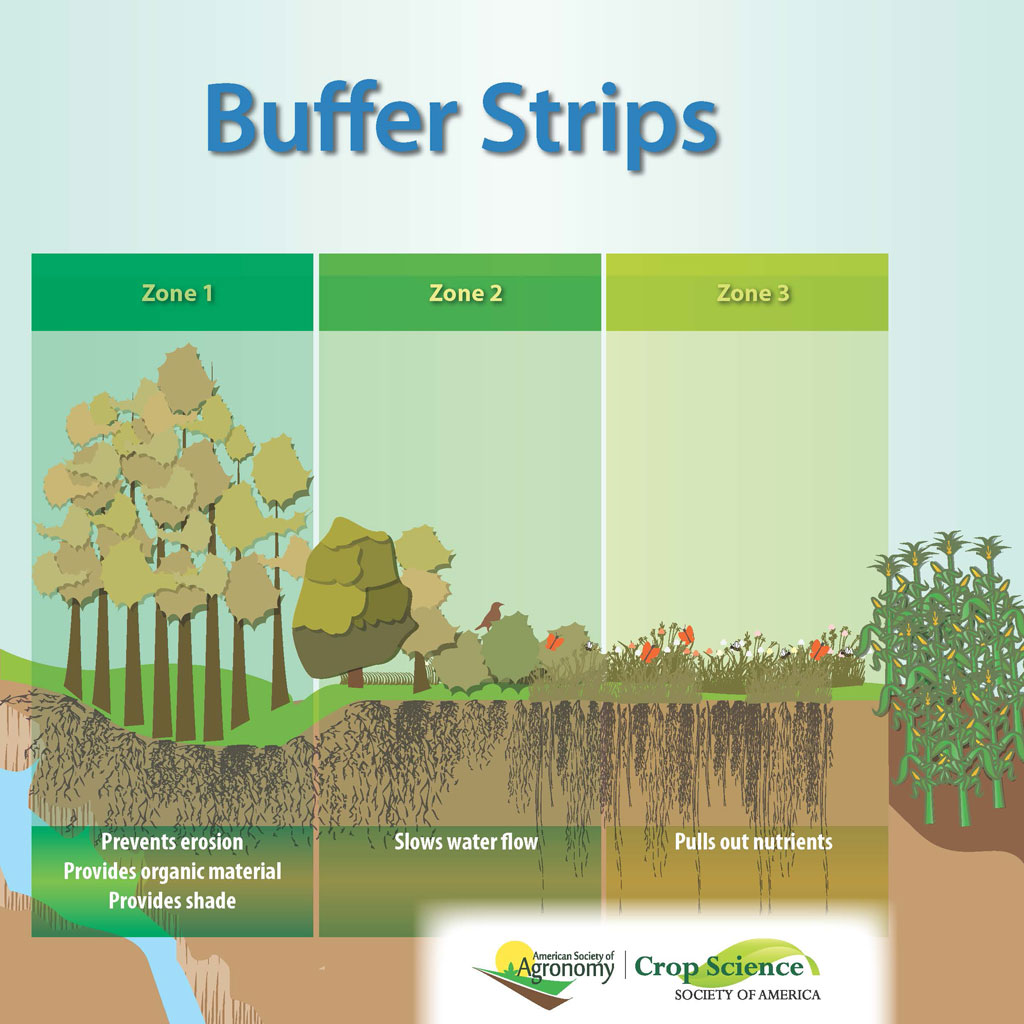
Riparian buffer strips typically contain three progressive zones of plants to filter groundwater and protect the environment. Together, these zones:
- reduce sediment loss from upslope terrain;
- provide shade and moderate temperature;
- maintain bank stability;
- recharge groundwater;
- protect aquatic habitat;
- provide wildlife habitat; and
- enhance nutrient uptake.
These benefits can apply to buffer strips near agricultural, industrial, or residential areas. For example, in the Pacific Northwest, riparian buffer strips are used to protect salmon populations from forest harvesting activity.
“Human use of land near streams can negatively impact the purity of the water,” Ramcharan says. “Riparian buffers are a primary tool for protecting freshwater ecosystems.”
To read the complete blog, visit Sustainable, Secure Food at https://wp.me/p9gkW1-3y.
American Society of Agronomy and Crop Science Society of America: Our members are researchers and trained, certified, professionals in the areas of growing our world’s food supply, while protecting our environment. We work at universities, government research facilities and private businesses across the United States and the world.




